MPLS is a network routing technique that directs data packets based on labels rather than network addresses. The routers encapsulate the data with a label containing information like wavelength or timeslot. The label is then popped off, and the underlying packet is routed as usual.
Digital transformation is vital for businesses but needs the proper infrastructure to maintain performance and visibility.
Cost-Effectiveness
A key benefit of digital transformation is that it helps businesses save money. For example, automating customer technical support can eliminate human errors and system failures that result in downtimes and lost revenue. Similarly, implementing low-code internal business process development tools can simplify processes and streamline operations. Moreover, the cloud offers a cost-effective way to scale business applications without expensive hardware.
In addition to being cost-effective, MPLS improves network quality of service (QoS). The technology segregates traffic based on its inherent nature and uses different packet labels to determine its path. This allows data packets with higher performance metrics like voice and video to be routed over lower-latency paths. This can help companies avoid bandwidth bottlenecks and ensure their users have a consistent communications experience.
However, it’s important to note that MPLS connections are more expensive than Internet access. They are also more challenging to deliver globally and require a private connection, which can be expensive to deploy and maintain. Many organizations leverage SD-WAN to augment or replace MPLS with low-cost broadband Internet. By doing so, they can gain better bandwidth and more scalable connectivity for remote locations. Additionally, SD-WAN can offload traffic from MPLS to the Internet, freeing up bandwidth and improving application performance.
Scalability
Unlike other packet-switching technologies tied to specific network protocols, what is MPLS allows you is to attach a “label” to data packets, indicating their forwarding class. This makes it easier for routers to decide how to route these packets, improving overall network performance.
Another advantage of MPLS is its scalability, which allows organizations to scale as their business grows. This is crucial for digital transformation projects, which typically involve multiple business units and require a centralized approach. These initiatives must be backed by solid adoption and change management strategies to ensure success.
MPLS is also more efficient than other packet-switching technologies, such as Ethernet. This lets you prioritize different data types and assign bandwidth percentages to each class. This improves performance, and it’s especially beneficial for latency-sensitive applications.
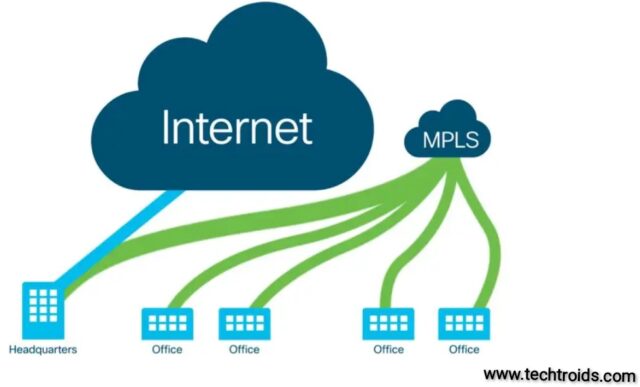
Historically, MPLS was best used for connecting remote branch offices to enterprise data centers. This was known as a hub-and-spoke network topology, and it relied on an MPLS connection to backhaul traffic to and from the data center. However, businesses have shifted to a more cloud-based model and rely less on the private MPLS connection. This has reduced the value of the technology, but many organizations still need to support their business-critical applications with reliable connections. This is where SD-WAN can come into play.
Reliability
Telecommunications companies need high-quality and reliable connectivity to ensure uninterrupted communication with consumers. Network downtime can have severe implications for the company, including lost revenue and decreased customer satisfaction. To avoid downtime, many telecommunications companies use Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) to provide network redundancy.
MPLS works at OSI layer 2 (data link) and layer 3 of the networking model, directing data packets based on labels rather than IP addresses. It is also protocol agnostic, working on top of any underlying network protocol. Labels are stacked, meaning routers don’t need additional IP lookups when they route data between each label. When a data packet reaches the egress router at the end of the path, the final label is “popped,” and the traffic goes through normal IP routing.
While MPLS is an excellent option for network reliability, it’s more flexible than other options. For example, it requires a private connection to the network, which takes time to scale or upgrade quickly. In addition, it’s not designed to connect to the cloud. Therefore, it’s best suited for connecting remote branch offices to enterprise data centers. In this case, it’s essential to consider a WAN strategy that includes both MPLS and SD-WAN to maximize network performance.
Flexibility
When a data packet enters an MPLS network, it is tagged with an identifier known as a label. The label tells the router where to send the packet next. Each router uses the label to look up its destination’s path in its routing table. This process speeds up data transfer and provides reliability.
The MPLS protocol allows organizations to control the bandwidth and latency of their networks. This is particularly important for real-time applications. MPLS is also ideal for enabling secure connections to the cloud.
In addition to accelerating data, MPLS offers a flexible connectivity solution for branch offices. It can be augmented with an SD-WAN or replaced entirely with the Internet to optimize branch networking decisions based on application, bandwidth, and security requirements. This allows organizations to better meet customer demands for a consistent, high-quality experience.
Unlike the public Internet, MPLS traffic is guaranteed to be delivered with no drops or delays. This is especially useful for high-value, mission-critical applications like Voice and video.